Occurrence Calculated Attributes
Using the Calculated Attributes feature, you can build formulas dynamically using available dRofus fields to create additional fields. Calculated Attributes are available for Rooms, Items, Occurrences, and Products and allow you to build simple to very complex results. We explain how to do this for Room and Room Template Calculated Attributes, Items Calculated Attributes, and Occurrence Calculated Attributes. The Calculated Attribute Formats are the same across dRofus. A good baseline understanding of how Item Composite Text Attributes work is a great place to start since the rules can be combined with these attributes.
To create composite text attributes, you need superuser access to the database, as the setup is done in the Administration settings. Please refer to Project and Database Administration.
Occurrence True/False and Value Example
Example:
Confirm the following two conditions before consider moving the occurrence forward into procurement:
If the product has a:
Document attached.
Unit price
Since we are working with an occurrence, we know that a room and an item have been defined. This example is checking across several modules at once. Two fields were added: Has document (yes/no) and Unit price.
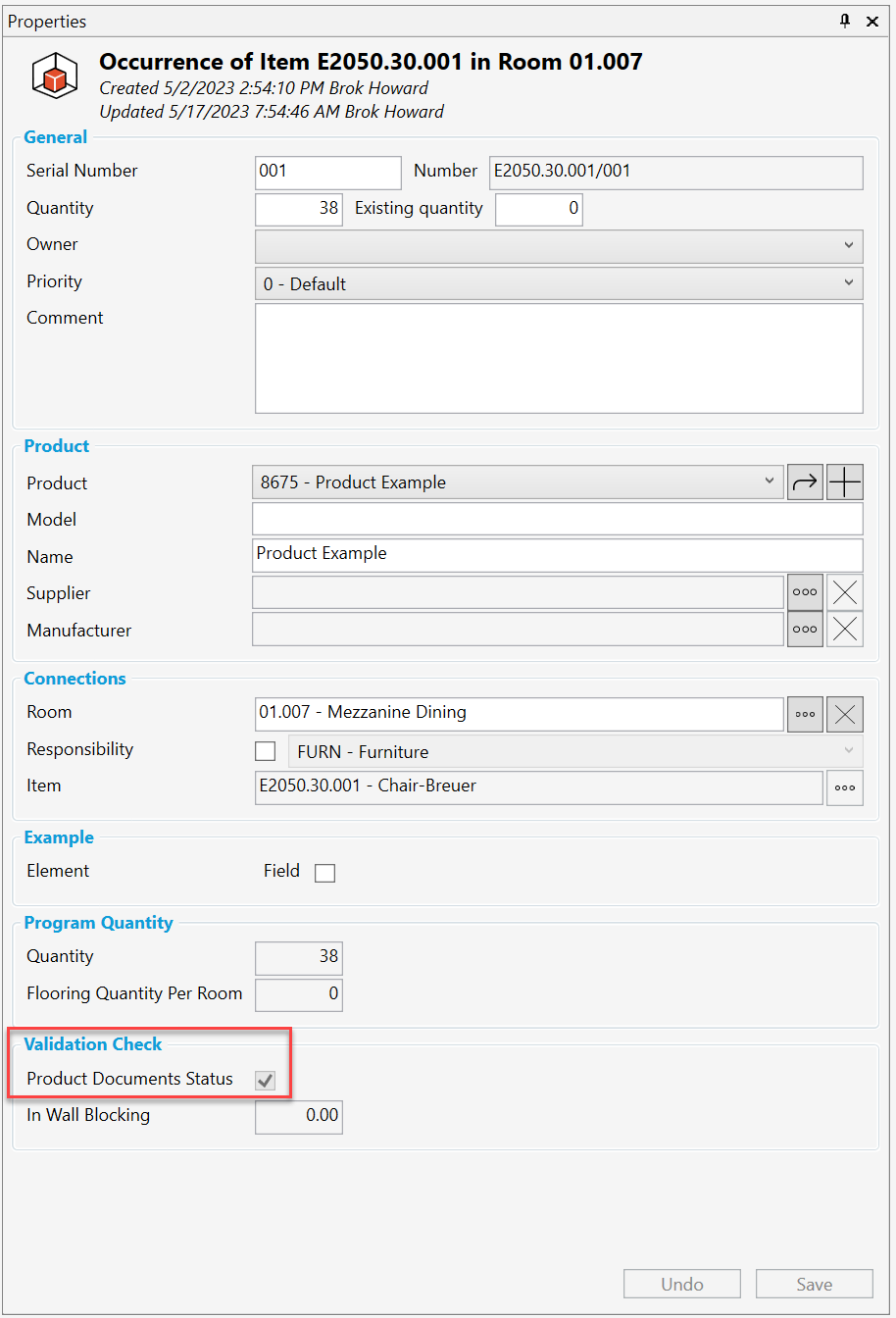
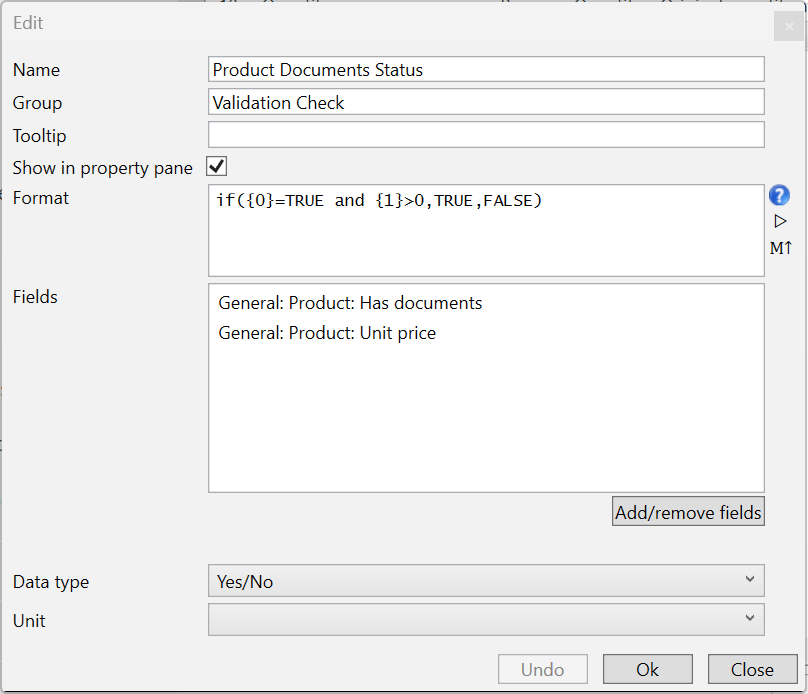
The first part is an if/then format that checks if the product has a document AND has a unit price greater than zero. If both are true, we return TRUE. If either is not valid, we return FALSE. The Data type is a Yes/No, so in the occurrence properties panel, we will see a check box under Product Documents Status within a new group called Validation Check. This could also be a column added to an occurrence list to quickly see which occurrences are ready for procurement or used in a report filter.
Most calculated attributes are designed around numbers, and our default formulas create a bracket around the field {0} when building out a formula. But sometimes, we like to use text, yes/no, or list values. For example, when checking whether two text fields match or both values are True. For these formulas to work, you need to add a single quote around the bracket ‘{0}’ so that we know it should be a string, not a number.
The most powerful feature of calculated attributes with occurrences is that you can access all room properties, room data fields, item properties, item data fields, product properties, product data fields, occurrence properties, occurrence data fields, documents, and image fields. We can’t wait to see what you uncover as you leverage this powerful feature.
Format | Summary | Example |
|---|---|---|
+ | Returns the sum of two numeric operands. (Addition) | {0} + {1} ~ 0:1, 1:4 = 5 |
- | Returns the difference of two numeric operands. (Subtraction) | {0} - 4 ~ 0:10 = 6 |
* | Returns the product of two numeric operands. (Multiplication) | {0} * {1} ~ 0:2, 1:3 = 6 |
/ | Returns the quotient of two numeric operands. (Division) | if ( {1} = 0, 0, {0} / {1} ) ~ 0:9, 1:3 = 3 |
and | Indicates whether both operands are true. | {0} < 10 and {0} > 0 ~ 0:5 = True |
or | Indicates whether either or both operands are true. | {0} < 2 or {0} >5 ~ 0:8 = True |
not | Returns true if the logical operand is false. | not ({0} < 0) ~ 0:-5 = False |
= | Indicates whether the left operand is equal to the right operand. | {0} = 4 ~ 0:4 = True |
!= | Indicates whether the left operand is not equal to the right operand. | {0} != {1} ~ 0:2, 1:4 = True |
< | Indicates whether the left operand is less than the right operand. | {0} < 0 ~ 0:2 = False |
<= | Indicates whether the left operand is less than or equal to the right operand. | {0} <=2 ~ 0:2 = True |
> | Indicates whether the left operand is greater than the right operand. | {0} > 0 ~ 0:8 = True |
>= | Indicates whether the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand. | {0} >= 5 ~ 0:10 = True |
if | Returns a value based on a condition | if ( {0} % {1} = 0, ‘Yes’, ‘No’ ) ~ 0:4, 1:2 = Yes |
in | Returns whether an element is in a list of values. | in ( {0}, {1}, {2}, {3} ) ~ 0:7, 1:4, 2:7, 3:9 = True In the example above, the first declared argument '{0}' is the value you want to evaluate, in this example, the number '7' as defined by the '0:7' after the (~). |
isNull | Returns true if the operand is null. | isNull ( {0} ) ~ 0: = True |
substring | Returns a slice of the provided text. The slice is decided by a start position and optional end position, starting from 0. | substring ( {0, 7) ~ 0:Doctor Rofus = Rofus |
contains | Returns true if the first text operand contains the second text operand. | contains ( {0}, {1} ) ~ 0:abc, 1:a = True |
length | Returns the number of characters in the text. | length ( {0} ) ~ 0:Hello = 5 |
replace | Replaces a substring in the first text operand. All matches of the second text operand are replaced with the third text operand. | replace ( {0}, {1}, {2} ) ~ 0:Hello, 1:l, 2:xx = Hexxo |
startsWith | Returns true if the first text operand starts with the second text operand. | startsWith ( {0}, {1} ) ~ 0:Hello, 1:H = True |
endsWith | Returns true if the first text operand ends with the second text operand. | endsWith ( {0}, {1} ) ~ 0:Hello, 1:o = True |
regexIsMatch | Returns true if the first text operand contains a match using the second text operand as a regular expression. | regexIsMatch ( {0}, ‘a.*’ ) ~ 0:abc = True |
regexReplace | Replaces a substring in the first text operand. All matches found using the second text operand as regular expression are replaced with the third text operand. | regexReplace ( {0}, ‘l+’, 'X' ) ~ 0:Hello = HeXo |
regexGroup | Returns the value of a regular expression group. Group index starts from 1 and defaults to 1 if not given. | regexGroup ( {0}, ‘(1+)’ ) ~ 0:Hello = ll |
Round | Rounds a value to the nearest integer or specified number of decimal places. | Round ( {0}, 2) ~ 0:3.1415 = 3.14 |
Floor | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to the specified number. | Floor ( {0} ) ~ 0:1.5 = 1 |
Ceiling | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the specified number. | Ceiling ( {0} ) ~ 0:1.5 = 2 |
Truncate | Calculates the integral part of a number. | Truncate ( {0} ) ~ 0:3.14 = 3 |
Abs | Returns the absolute value of a specified number. | Abs ( {0} ) ~ 0:-1 = 1 |
Min | Returns the smaller of two numbers. | Min ( {0}, {1} ) ~ 0:-4, 1:23 = -4 |
Max | Returns the larger of two numbers. | Max ( {0}, {1} ) ~ 0:5, 1:8 = 8 |
Sqrt | Returns the square root of a specified number. | Sqrt ( {0} ) ~ 0:4 = 2 |
Pow | Returns a specified number raised to the specified power. | Pow ( {0}, 2) ~ 0:3 = 9 |
Exp | Returns e raised to the specified power | Exp ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 1 |
Log | Returns the logarithm of a specified number. | Log ( {0}, 10) ~ 0:1 = 0 |
Log10 | Returns the base 10 logarithm of a specified number. | Log10 ( {0} ) ~ 0:1 = 0 |
Sign | Returns a value indicating the sign of a number. | Sign ( {0} ) ~ 0:-10 = -1 |
Sin | Returns the sine of the specified angle. | Sin ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 0 |
Cos | Returns the cosine of the specified angle. | Cos ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 1 |
Tan | Returns the tangent fo the specified angle. | Tan ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 0 |
Asin | Returns the angle whose sine is the specified number. | Asin ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 0 |
Acos | Returns the angle whose cosine is the specified number. | Acos ( {0} ) ~ 0:1 = 0 |
Atan | Returns the angle whose tangent is the specified number. | Atan ( {0} ) ~ 0:0 = 0 |
.png)